Designing Highly Available Web Solutions
with Microsoft Windows 2000 Server Technologies
This exam tests your ability to design Web solutions that
incorporate Microsoft Windows 2000 Server technologies. The
expected scenarios have the following characteristics:
- Concurrent client connections that can exceed 1,000
- Transactional applications
- User databases, such as LDAP server or directory
service
- Internet security, such as firewalls, secure
protocols, or proxy servers
- High availability services that can include Network
Load Balancing (NLB), Component Load Balancing (CLB),
Cluster service, and Microsoft Application Center 2000
When you pass this exam, you achieve Microsoft Certified
Professional status. You also earn credit toward the
following certifications:
- Core or elective credit toward Microsoft Certified
Systems Engineer on Microsoft Windows 2000 certification
A lot of the information in
this study guide is useful for the 70-223 exam as well. You
should study both before attempting the exam.
Key Concepts
Availability
- a measure with a range from 0 to 100 percent
- about fault tolerance of a computer and its programs
- 24 hours a day, 7 days a week is the goal
Failure
- departure from expected behavior
- can include behavior that moves outside of the defined
performance parameters
- possible types of failures can cause system outages:
- software failures
- hardware failures
- network failures
- operational failures
- environmental failures
Fault tolerance
- the ability to continue functioning when part of the
system fails
- problems can include:
- disk failures
- power outages
- corrupted operating systems
Manageability
- the ability to make changes to the system easily
- management disciplines include:
u
change and configuration management
u
security management
u
performance management
u
problem management
u
event management
u
batch/output management
u
storage management
Reliability
- measure of the time that elapses between system
failures
- hardware and software components have different
failure characteristics
- can use formulas that based on historical data exist
to predict hardware reliability
- hard to find formulas for predicting software
reliability
Scalability
Fundamental strategies for high availability
- Prepare well documented and appropriate operational
procedures
- Prepare enough capacity to handle processing loads.
- Reduce the probability of failure:
u
use architecture based on redundant,
load-balanced servers
u
review code to avoid potential problems such
as buffer overflows, infinite loops, code crashes, and
openings for security attacks
N-Tier architecture According to webopedia.com,
"N-tier application architecture provides a model for
developers to create a flexible and reusable application. By
breaking up an application into tiers, developers only have
to modify or add a specific layer, rather than have to
rewrite the enitire application over, if they decide to
change technologies or scale up. In the term "N-tier," "N"
implies any number -- like 2-tier, or 4-tier; basically, any
number of distinct tiers used in your architecture."
Architectural elements:
- Clients - issue service requests to the server hosting
the application
- Front-end systems - servers that provide core
application services
- Back-end systems - servers hosting the data stores
used by the front-end systems
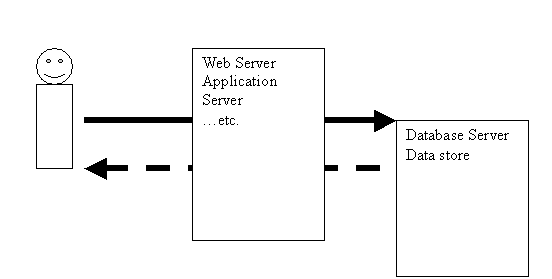
Infrastructure Strategies
DNS
Internet connection
- the first step in modifying the network topology to
increase availability is to add a redundant connection to
the Internet
Cluster Management
- Configure an independent management subnet for
connecting to each cluster
DHCP high availability without clustering
- set up a primary DHCP server and a backup DHCP server
- use the 80/20 rule to divide scope addresses between
the DHCP servers
u
primary server receives about 80 percent of
the available addresses
u
backup server receives about 20 percent of
the available addresses
Server hardware
- Each server should have the following redundant
components:
u
NICs
u
Cooling fans
u
Power supplies
u
Disk controllers
- server room should have a room temperature about 70 F
(21 C)
- server room should have a proper amount of humidity
maintained
- server room should be kept clean.
- for a data storage system that is fault tolerant and
data centralized, use Storage area network (SAN):
u
high-speed subnetwork of shared storage
devices
u
storage device - machine that contains
nothing but only disks for storing data
u
all storage devices are available to all
servers on a LAN or WAN
u
stored data does not reside directly on any
of a network's servers
u
server merely acts as a pathway between the
end user and the stored data.
According to webopedia.com, RAID is
"Short for Redundant Array of Independent (or
Inexpensive) Disks, a category of disk drives that employ
two or more drives in combination for fault tolerance and
performance. RAID disk drives are used frequently on servers
but aren't generally necessary for personal computers."
RAID capable of fault tolerance are:
u
data is written to two duplicate disks
simultaneously
u
if one of the disk drives fails, the system
can instantly switch to the other disk
u
prevent any loss of data or service
u
limited scalability
u
slower write performance
u
does not use space efficiently
- Level 5: data striping at the byte level and also
stripe error correction information.
Application Center 2000
- Maintains high level of web service availability
- Allows Web site administrators to group Windows 2000
Server computers into clusters for easy management
- Divides Web site content and code into applications
that can be updated independently. each server in the
cluster hosts a copy of the application,
- Application Center does the synchronization
- Support clusters made of Windows 2000 Server computers
|
Feature
|
Description
|
| Cluster services |
For administering the
cluster configuration via wizards or GUI. |
| Load balancing |
Integrated NLB and CLB.
|
| Synchronization and
deployment |
System settings,
content, and applications are replicated either
automatically or on demand. |
| Monitoring |
Real-time event,
performance, and health monitoring. |
| Programmatic support
|
Scripting support for
performing common Application Center management tasks.
|
| Local and remote
administration |
Administration via local
access or through secure remote connection. |
| High availability |
Requests and
transactions are automatically rerouted to another
member in case of server failure. |
Server cluster and NLB
- Primary clustering scenarios
u
Single-node clusters
u
Standard Web clusters
u
COM+ applications clusters
- Single-node configuration
u
organize resources for administrative
convenience
u
use virtual servers
u
restart applications automatically
u
can easily create a cluster later
u
no failover
- Active/passive configuration
u
maximum availability for your resources
u
requires expensive investment in hardware
u
should the primary node fails, the secondary
node immediately picks up all operations
u
best suited for those applications and
resources that must maintain the highest availability
- Active/active configuration
u
high availability when both nodes are online
u
high performance when both nodes are online
u
reliable and acceptable performance when one
node is online
u
services remain available during and after
failover although performance can decrease
- Cluster service can manage:
u
Server cluster networks
u
Network interfaces
u
Nodes
u
Resource groups
u
Resources
u
logical collections of resources
u
made up of logically related resources, such
as applications and their associated peripherals and data
u
any physical or logical component that can
be brought online and taken offline
u
can be managed in a server cluster
u
can be owned by only one node at a time
u
when planning the resource groups for a
cluster on your network,
u
you should list the dependencies for each
resource
u
dependency list should include all resources
that support the core resource.
- Running applications on NLB
u
NLB can scale any application or service
that uses TCP/IP
u
the application must be designed to allow
multiple instances to run simultaneously
u
don't use NLB to directly scale applications
that independently update inter-client state data
u
IIS is an ideal application to run on NLB
u
SQL Server and Exchange Server should not be
run on the NLB cluster because they independently update
inter-client state data. You should use the Cluster
service for them instead.
u
Single network adapter in unicast mode:
l
works with all routers
l
ordinary network communication among hosts
isn't possible
l
network performance may be compromised.
u
Multiple network adapters in unicast mode:
l
works with all routers
l
ordinary network communication among hosts
is possible
l
network performance may be enhanced
l
at least two network adapters are required.
u
Single network adapter in multicast mode:
l
Only one network adapter is required
l
ordinary network communication among hosts
is possible
l
network performance may suffer
l
some routers may not support multicast MAC
address
u
Multiple network adapters in multicast mode:
l
Performance may be enhanced
l
ordinary network communication among hosts
is possible
l
at least two network adapters are required
l
some routers may not support multicast MAC
address
u
NLB pins a client to a particular host
without setting a timeout limit
u
mapping is in effect until the cluster set
changes
u
in a large site with multiple proxy servers
a client can appear to come from different IP addresses
u
all clients within a given Class C address
space will map to a given cluster host
u
does not address situations in which proxy
servers are placed across Class C address spaces
u
when enabled, NLB directs all TCP
connections from one client IP address to the same cluster
host
u
allows session state to be maintained in
host memory
u
should a server or network fail, a new logon
is likely required to reauthenticate the client and
reestablish the session state
CLB
- an Application Center feature
- provides dynamic load balancing for COM+
application components
- to enable CLB, an Application Center COM+
application cluster must activate components when requests
are received
- Application Center Web cluster and COM+
routing cluster are the same in terms of functionality -
both support CLB and can route requests to a COM+
application cluster.
- scenarios suitable for CLB:
u
You want to segregate COM objects behind an
additional firewall.
u
You want to run large COM objects on the
fastest servers available.
u
You're using NLB for your front-end servers
and you need to route component requests to a back-end
COM+ server
u
Component Object Model
u
A model for binary code
u
Developed by Microsoft
u
Allows programmers to develop objects that
can be accessed by any COM-compliant application
u
OLE, ActiveX and many other new web
technologies are based on COM.
u
COM+ is the next generation of COM
Multiserver environment for running applications
u
Supports a unified namespace.
u
You can isolate back-end servers from
attacks.
u
You can isolate processing tasks.
u
Gives room to scale out and make fault
tolerant.
u
network traffic
u
performance
u
availability
u
scalability
u
interchange of incoming requests and
outgoing responses between two points
u
often unpredictable
u
often occurs in bursts and clumps
u
to determine the maximum rate of pages per
second that your network can support, divide the bits per
second of the network connection by the bits generated for
the page request.
When you plan your
infrastructure, always take into account the capacity of the
internet link! Know the size of your web pages. Compare the
sizes with the available bandwidths and determine whether
additional capacity is needed!
|
Connection Type
|
Connection Speed
in theory |
|
Dedicated
Point-to-Point Protocol/ Serial Line Internet Protocol
(PPP/SLIP) using a modem |
28.8 Kbps
|
|
Frame Relay or fast
modem |
56 Kbps |
|
Integrated Services
Digital Network (ISDN) |
128 Kbps
|
|
Typical digital
subscriber line (DSL) |
640 Kbps
|
|
Digital signal level
1 (DS1)/T1 |
1.536 Mbps
|
|
10-Mb Ethernet
|
8 Mbps |
|
Digital signal level
3 (DS3)/T3 |
44.736 Mbps
|
|
Optical carrier 1
(OC1) |
51.844 Mbps
|
|
100-Mb Ethernet
|
80 Mbps |
|
Optical carrier 3
(OC3) |
155.532 Mbps
|
|
Optical carrier 12
(OC12) |
622.128 Mbps
|
|
1-Gbps Ethernet
|
800 Mbps
|
Security
- IIS authentication models:
u
Anonymous
u
Basic
u
Integrated Windows
u
Digest
u
Client certificate mapping
u
allows all Web clients to access a site
u
works with most browsers
u
uses the IUSR_computername account to
provide anonymous users with the right to log on locally
u
no authentication
u
if password synchronization is enabled,
Anonymous access can't access remote resources
u
requires that a user provide credentials in
order to log on
u
Users must have local logon rights to the
Web server
u
passwords are not securely encrypted
u
you can use Basic authentication along with
SSL for better security
- Integrated Windows authentication
u
more secure than Basic authentication
u
supports NTLM authentication
u
supports Kerberos authentication
u
cannot be used through proxy server
connections
u
support only the later versions of IE
u
encrypts passwords before transmission
u
can be used through proxy server connections
u
supported only for Windows 2000 domains
u
support only the later versions of IE
u
requires Active Directory.
- Client certificate mapping
u
authenticate users by mapping certificates
to Windows 2000 user accounts
u
two types of certificate mapping: one-to-one
and one-to-many.
u
very scalable
u
very secure
u
not easy to configure
u
not all browsers support it
u
an Internet standard commonly used to
encrypt data.
u
applications that use SSL must be SSL-aware
u
supports authentication through the use of
public key certificates
u
requires considerable processor resources
u
works at the IP layer of the TCP/IP protocol
stack
u
transparent to most applications
u
offers a high level of protection for most
applications and services
u
requires more processor power than SSL.
u
supports authentication through:
- Kerberos
- public key certificates
- preshared key values
u
computers on both ends of the communication
link:
- must be configured with Windows 2000
- must have IPSec security policies defined
- EFS
u
for protecting sensitive data stored on a
local disk
u
does not protect data transmitted over a
network
u
does not protect remotely stored data
Measuring availability
|
Bandwidth usage
|
n
peak bandwidth use
n
idle bandwidth use
n
how usage increases |
|
Network availability
|
n
use ICMP echo pings to check availability |
|
System availability
|
n
Monitor normal and abnormal shutdowns of
the system. |
|
HTTP availability
|
n
Monitor HTTP requests that are:
u
issued internally
u
issued from the ISP networks
u
issued from different geographic
locations around the globe
|
|
Performance metrics
|
n
number of visits
n
latency of requests for set of operations
and page groups
n
CPU utilization
n
disk storage
n
disk I/O
n
fiber channel loop bandwidth
n
memory usage
...etc |
Reference Books
McSe Designing Windows 2000 Web Solutions
Study Guide : Exam 70-226
Inc. Syngress Media (Editor); Paperback
|